How To Find Marginal Opportunity Cost
Define marginal opportunity cost (MOC) along a PP curve.
Define marginal rate of transformation (MRT)?
What does increasing MOC along a PP curve hateful?
(b) • Why does MOC increase?
(a) Marginal Opportunity Price. MOC of a item good (say wheat) along a PP bend is the corporeality of the other good (say tanks) which is sacrificed to produce an additional unit of that detail practiced. The charge per unit of this sacrifice is called marginal opportunity cost of the expanding good. Rate of sacrifice is technically termed every bit marginal rate of transformation (MRT).
MRT is the ratio of units of one good (say, tanks) that needs to be sacrificed to produce ane more unit of measurement of the other skilful (say, wheat). Symbolically :
![]()
| MARGINAL OPPORTUNITY Cost / MRT SCHEDULE | |||||
| Production Possibilities (or combinations) | Wheat (W) (lakh tons) | Tanks (T) (thousands) | MOC of wheat (in thousand tanks) | ||
| A | 0 | 15 | — | — | |
| B | one | xiv | 1·(= 15 - 14) | 1W : 1T | |
| C | 2 | 12 | 2·(= 14 - 12) | 1W : 2T | |
| D | 3 | 09 | 3·(= 12 - 9) | 1W : 3T | |
| Eastward | 4 | 05 | 4·(= 9 - 5) | 1W : 4T | |
| F | v | 00 | 5·(= 5 - 0) | 1W : 5T | |
A close look at the to a higher place table reveals that as product of wheat is increased, its marginal opportunity cost (MOC) in terms of tanks goes on increasing, i.east., MRT is ascent. For example, when order moves from combination A to B, it sacrifices 1 (= fifteen - 14) thousand tanks to produce 1 (= 1 - 0) lakh ton of wheat. Thus MOC of 1 lakh ton of wheat is 1 1000 tanks in the beginning, i.e., MRT = 1 : 1. Likewise in combinations C, D, Due east and F, MOC of producing one lakh ton of boosted wheat is ii (= 14 -12) thousand, iii(= 12 - ix) g, four(= nine - 5) thousand and five(= v - 0) k tanks respectively. In brusque for every unit increase in production of wheat, more than and more tanks are to be sacrificed, i.e., marginal opportunity toll, i.due east., MRT goes on increasing. But why does MOC increase? Following are its two master reasons.
(b) Reasons for increasing marginal opportunity cost (or MRT)
(i) Operation of police force of diminishing returns (or increasing cost). According to this law, if more than and more than units of a good are to be produced, the boosted units will require more than and more of factors units, i.e., price of production of additional units of the good will increase.
(ii) Transferring resources from more productive to less productive uses. Various resources are specialised in production of dissimilar appurtenances. When factors (resource) which are specialised for product of a particular good (say, workers manufacturing tanks) are transferred to the production of another skilful (say, production of wheat) for which they are less productive, some productivity is lost. Therefore, more of such resources (say workers) are needed to produce an additional unit of other proficient. This implies increment in marginal opportunity cost making the PP bend concave in shape.
What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Distinction between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
Briefly put (i) Microeconomics is the study of individual economic units like a consumer, a business firm (producer) whereas macroeconomics is the study of economy equally a whole and its aggregates like national income, total employment, full general price level.
(2) Central problems of microeconomics is price conclusion and resource allotment of resources but that of macroeconomics is determination of level of income and employment.
(three) Main tools of microeconomics are demand and supply of the detail commodity/ cistron whereas tools of macroeconomics are aggregate demand and amass supply of the whole economic system.
(iv) Microeconomics analyses how equilibrium of a consumer, a producer or an industry is attained but macroeconomics is concerned with determination of economy's equilibrium level of income, employment and output.
(v) Microeconomics deals with determination of prices of individual goods and individual factors of production simply macroeconomics deals with general price level and nation'south incomes.
(half dozen) Microeconomics explains how resources are allocated and how full product is distributed among cooperating factors of product but macroeconomics explains how productive capacity and national income of a country increment overtime.
Explain the central problem 'for whom to produce.'
The problem for whom to produce refers to selection of the category of people who will ultimately consume the goods. Since resources are deficient in every economy, no gild can satisfy all the wants of its people. Thus, a problem of pick arises. The economic problem of "For whom to Produce" basically focuses on the distribution mix of the final goods and services produced. The distribution of the final goods and services is equivalent to the distribution of National Income (or National Product) among the factors of product such equally land, labour, capital and entrepreneur.
The problem can be categorised nether 2 main heads:
(i) Personal Distribution: It means how national income of an economy is distributed amidst different groups of people.
(two) Functional Distribution: It involves deciding the share of different factors of production in the total national product of the land. Guiding Principle of 'For whom to Produce': Ensure that urgent wants of each productive factor are fulfilled to the maximum possible extent.
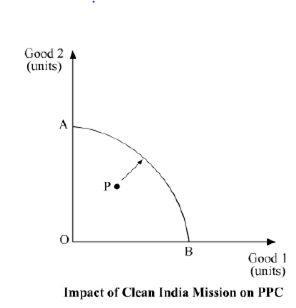
What will be the touch of recently launched 'Clean India Mission' (Swachh India
Mission) on the Production Possibilities curve of the economy and why?
Or
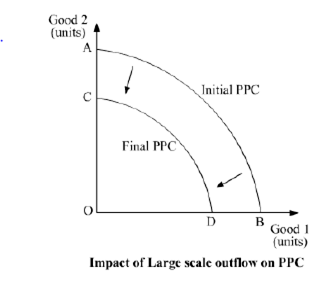
What will probable be the touch on of big scale outflow of foreign capital on Production
Possibilities bend of the economic system and why?
Production possibility curve is a graphical representation of the maximal mix of outputs
that an economy tin can achieve using its existing resources to total extent and in the most
efficient mode. The mission of 'Clean Republic of india Mission' (Swachh Republic of india Mission) will atomic number 82 to
improve waste matter-management technique. Consequently information technology leads to healthy India and increased
individual productivity. Both these factors will lead to better and efficient utilisation of
existing resources of an economic system. Appropriately, the economy will movement college and closer
to initial PPC. This motion is being depicted in the beneath graph with the aid of the
arrow from betoken P.
OR
The large calibration outflow of foreign uppercase will lead to a decrease in the availability of
resources, thereby shifting the Production Possibility Bend (PPC) from correct to left that is
from AB to CD as shown in the following diagram. Hence, nosotros can say that leftward shift of
PPC results in autumn in output and resources.
Source: https://www.zigya.com/study/book?class=12&board=cbse&subject=Economics&book=Introductory+Microeconomics&chapter=Introduction&q_type=&q_topic=&q_category=&question_id=ECEN12043224
Posted by: hernandezwinger.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Marginal Opportunity Cost"
Post a Comment